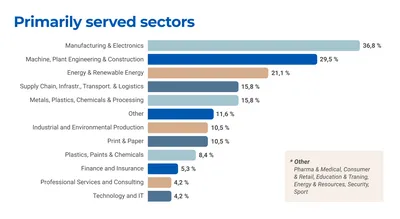
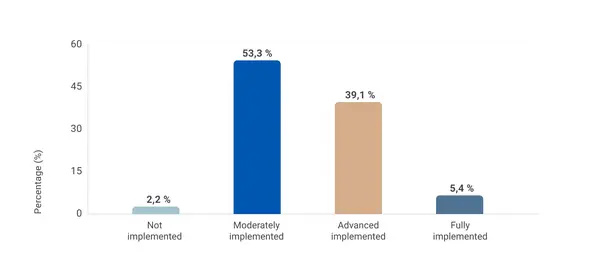
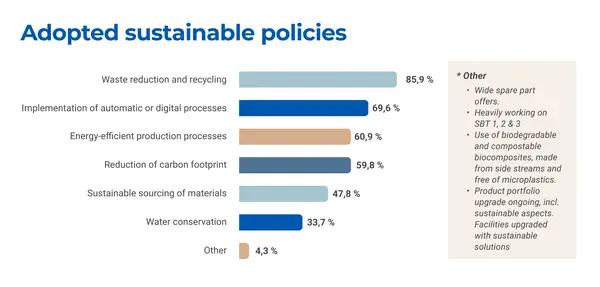
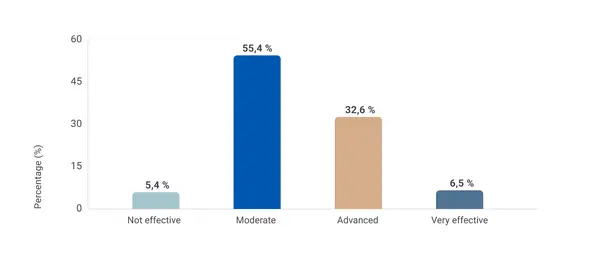
This report presents the findings of a global external survey conducted by Kestria Industrial/Production Practice Group to explore the current state of sustainable production practices across diverse industrial sectors. The survey aimed to gather actionable insights to help organisations assess their practices, identify areas for improvement and uncover the most effective approaches to reducing environmental impact. It also sought to assess the awareness, attitudes and motivations of decision-makers and the barriers to progress towards sustainable operations. Additionally, the survey compared efforts across sectors to highlight best practices and emerging opportunities.
The objectives of the survey were:
- Assess the current implementation of sustainable production practices: Understand how organisations are adopting and integrating sustainability into their operations.
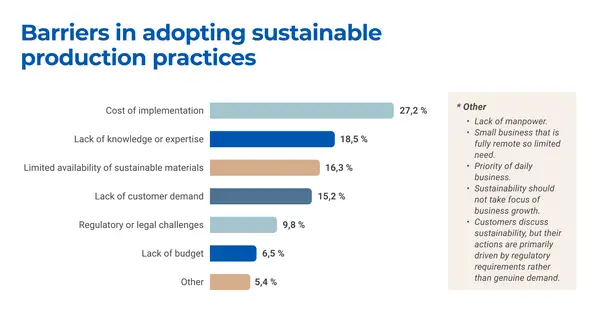
- Identify barriers to progress: Highlight the challenges that limit the adoption of sustainable practices, including cost, resource constraints and external market factors.
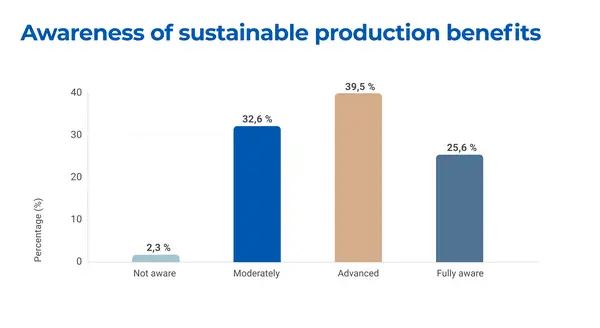
- Measure awareness and attitudes: Evaluate the understanding and commitment of decision-makers toward the benefits of sustainability.
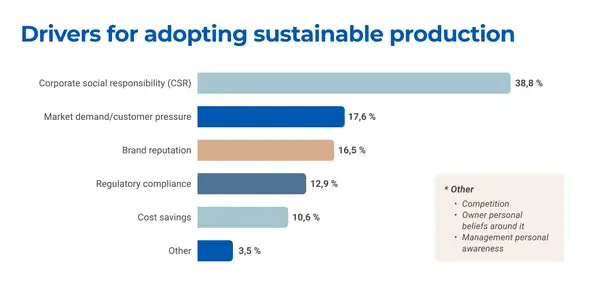
- Explore motivations and drivers: Examine the key factors encouraging organisations to adopt sustainable practices, including corporate social responsibility, regulatory compliance and market demand.
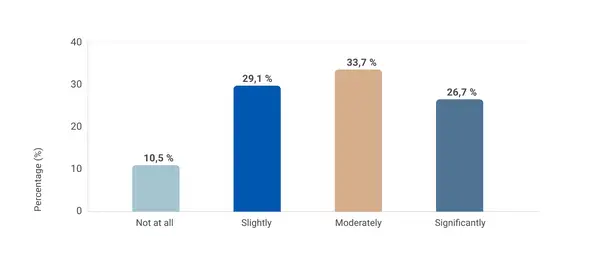
- Uncover opportunities for improvement: Gather insights into innovative strategies, technologies and partnerships that can drive sustainability efforts further.